- contact@vision-surgery.ai
- 548 Market St PMB 24044 San Francisco, California 94104-5401
Machine Learning for Surgical Phase Recognition
Four surgical phases of our focus

Surgical Phase
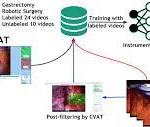
One of the most commonly studied applications of ML to intraoperative video analysis is the surgical phase recognition, and this has been the foundation of ML in surgery.

Instrument Recognition
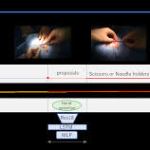
Another application of computer vision for video analytics is surgical instrument recognition. Although instrument recognition might not seem to be intuitively useful, the choice of the surgical tool can provide contextual cues to surgical phase and as such contribute to more accurate analysis of surgical procedure complexities and surgeon proficiency.

Gesture Recognition
Gesture and movement recognition is an extension of both the surgical phase and surgical instrument recognition. While previously mentioned intrument tracking in principle foucuces on the surgical equipment spatiotemporal behaviour, gesture recognition goes a step further and combines prviously mentioned features.

Anatomical Landmark Recognition
Recent and interesting adddition to ML in surgery is the ability to identify surgical anatomy using laparoscopic cholecytectomy procedures. These models could provide intra-operative augmented reality feedback to surgeons, particularly trainees, enabling real-time decision-support and enhancing patient safety.